This section explains the moving-bed method, which is one of the ways by
which the fixed-bed system can be made continuous.
 |
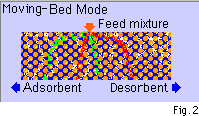
| Let us say that in Fig. 1, the adsorbent is caused to move in the opposite
direction of the desorbent (and component A, C) at a migration rate between
the velocities of components A and C. This would be the situation in Fig.
2, where while the desorbent is continuously fed into one end of the column,
the adsorbent is made to move in the direction opposite to that of the desorbent,
while the feed mixture is also supplied at the middle of the adsorbend bed.
At this point the adsorbent is caused to move at a migration rate, Us, which
is between Ua and Uc, the velocities of components A and C in the fixed-bed
mode, i.e. (Ua>Us>Uc). |

 |
We recommend the use of
the following internet browsers:
Internet Explorer(ver. 3.02 or above)
and Netscape Communicator(ver.4.06 or above). |

In such a situation, components A and C will move within the column at
the speeds, Ua-Us (>0) and Uc-Us (<0) respectively. Thus, starting
from the point where the feed mixture is fed, components A and C will move
in opposite directions from one another within the column. If the mixture
is continuously fed into such a device, components A and C will continuously
be separated to both ends of the column. However, in a large industrial
device, it is extremely difficult to uniformly move the adsorbent without
disturbing the absorption band. |

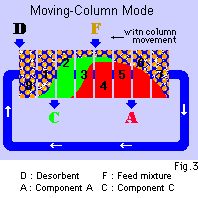
From this conception came the idea that rather than have the adsorfent
continuously move, instead a column of fixed length (packing bed) could
move. This process is shown in Fig. 3.
With a device such as the one described in the preceding paragraph, a
mixture can be separated in a continuous manner using the principle of the
moving-bed mode. While it is not impossible to move the column in smaller
devices, in an industrial device, it becomes mechanically complex.
The simulated moving-bed mode described in the following section is a
chromatographic separation method invented so as to gain the same level
of separation as the moving-bed mode, without having to actually move the
adsorbent. |

 |
We recommend the use of
the following internet browsers:
Internet Explorer(ver. 3.02 or above)
and Netscape Communicator(ver.4.06 or above). |

|